Lens
Lens is a front-end web component library for building search tools in the medical space to answer questions such as:
What is the age distribution of patients with lung cancer across participating hospitals?
It is used at Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum to build tools for cancer research such as the BBMRI-ERIC Locator and the CCP Explorer.
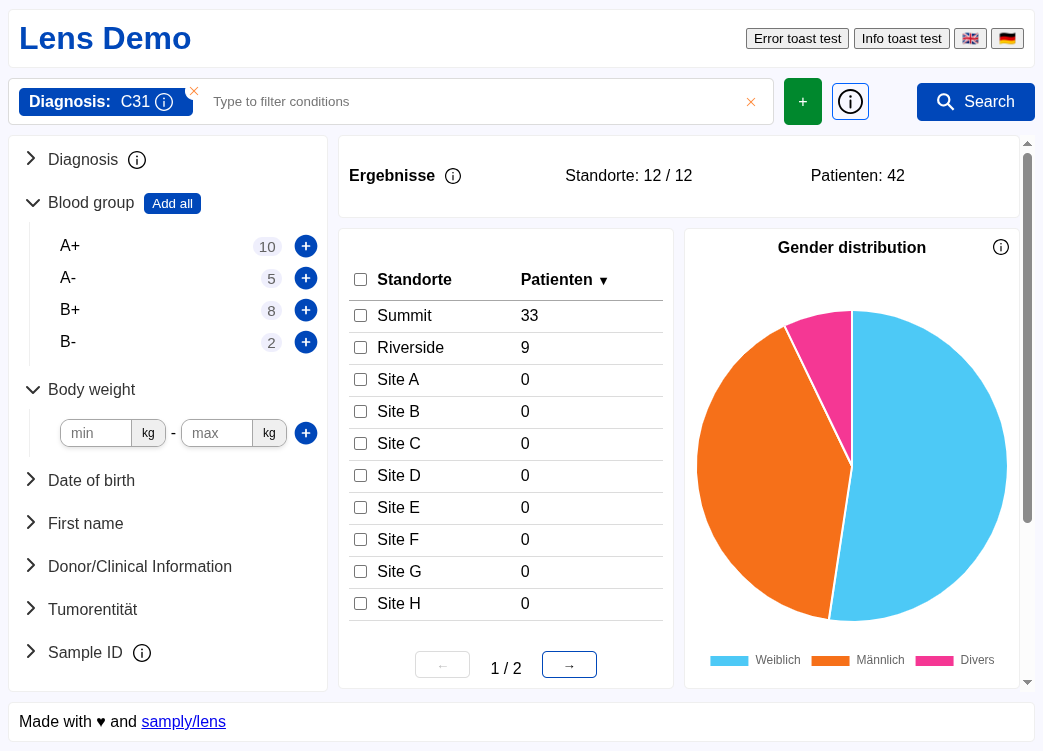
You can try out the interactive demo that showcases the functionality of a typical Lens-based application. Note that in the demo results are hardcoded and do not reflect your query.
Documentation
Get started with Lens by following the creating a new application guide. The guide is part of the Lens Book which is split into these chapters:
- User Guide for users of the Lens library
- Development for developers and contributors
- Components with docs for the individual web components
- Release notes for releases and migration guides
Documentation for the TypeScript API of Lens is available as TypeDoc.
Development
To get started working on Lens clone the repository and run:
npm install
npm run dev
This will start the demo application that you can use to test your changes to the web components and library.
Refer to the development chapter of the Lens Book for more information.
User Guide
This guide will help you set up your exploration tool using Lens.
We recommend starting with a new application using the new-app guide, followed by connecting your data source as described in the query documentation and passing results to Lens as shown in the showing results guide. Documentation for all available components
To customize the appearance of lens components, refer to the overwriting styles guide for instructions on how to apply your own styles.
Creating a new application
Lens is framework agnostic, so there are many ways to build and deploy your application. This guide focuses on compatibility with other projects in the Samply organization, so we use SvelteKit as the frontend framework and Docker for deployment.
To create a new SvelteKit application run npx sv create my-app. Use the minimal template with TypeScript syntax and select Prettier and ESLint when prompted.
Now cd to the new directory and install Lens:
npm install @samply/lens
Prettier config
The Prettier config created by sv create uses tabs and sets the print width to 100 against the recommendation of Prettier. We recommend to remove these options from .prettierrc and use the Prettier defaults with the Svelte plugin only:
{
"plugins": ["prettier-plugin-svelte"],
"overrides": [
{
"files": "*.svelte",
"options": {
"parser": "svelte"
}
}
]
}
Configuring the root route
Typically your application will only use the root route at src/routes. We will import the Lens CSS and JS bundles and render the main application component. Because Lens uses Web Components we need to disable HMR and SSR. Change the content of src/routes/+page.svelte to:
<script lang="ts">
// Using hot module replacement (HMR) with custom elements (aka web
// components) does not work because a custom element cannot be updated once
// registered, see https://github.com/WICG/webcomponents/issues/820.
// Therefore we do a full page reload instead of HMR.
if (import.meta.hot) {
import.meta.hot.on("vite:beforeUpdate", () => {
window.location.reload();
});
}
// Import Lens CSS and JS bundles
import "@samply/lens/style.css";
import "@samply/lens";
import App from "../App.svelte";
</script>
<App />
And add src/routes/+page.ts:
// Using server-side rendering (SSR) with custom elements (aka web components)
// causes issues because the server does not know that an element is a Svelte
// component and converts all props to strings.
export const ssr = false;
Note that the route files +page.svelte and +page.ts require the + prefix.
The application component
Your main application code lives in the application component. Create the file src/app.css and leave it empty and create src/App.svelte with the following content:
<script lang="ts">
import "./app.css";
</script>
<lens-search-button></lens-search-button>
Now run npm run dev and open http://localhost:5173/ in your browser. You should see a search button in the top left corner of the page.
Options and catalogue
Your application must pass two objects to Lens. The LensOptions object contains general configuration options and the Catalogue object describes what users can search for. You can define these objects in TypeScript but many applications in the Samply organization define them in JSON files.
Assuming you are using JSON files, create the file src/config/options.json containing the empty object {} and the file src/config/catalogue.json with the following content:
[
{
"key": "rh_factor",
"name": "Rh factor",
"fieldType": "single-select",
"type": "EQUALS",
"criteria": [
{
"key": "rh_positive",
"name": "Rh+"
},
{
"key": "rh_negative",
"name": "Rh-"
}
]
}
]
Add the following to the top of src/App.svelte to load the JSON files and pass the objects to Lens:
<script lang="ts">
import { onMount } from "svelte";
import {
setOptions,
setCatalogue,
type LensOptions,
type Catalogue,
} from "@samply/lens";
import options from "./config/options.json";
import catalogue from "./config/catalogue.json";
onMount(() => {
setOptions(options as LensOptions);
setCatalogue(catalogue as Catalogue);
});
</script>
<lens-search-bar></lens-search-bar>
<lens-catalogue></lens-catalogue>
When you run npm run dev you should see the search bar and the catalogue component with the “Rh factor” entry. Open the “Rh factor” entry and click the plus icons next to Rh+ and Rh- in order to add them to the search bar.
NOTE: The options.json file is being initialized with an empty object for now, but will be populated in the later parts of this book. Whenever the book tells you to add something to the Lens options it is implied that you add it to this file.
Schema validation
Lens includes JSON schema definitions for the options and the catalogue type. Create the script scripts/validate-json-schema.bash to validate your JSON files against the schema definitions:
set -e # Return non-zero exit status if one of the validations fails
npx ajv validate -c ajv-formats -s node_modules/@samply/lens/schema/options.schema.json -d src/config/options.json
npx ajv validate -c ajv-formats -s node_modules/@samply/lens/schema/catalogue.schema.json -d src/config/catalogue.json
Then install the required dependencies and test the script:
npm install ajv-cli ajv-formats --save-dev
bash scripts/validate-json-schema.bash
You can also configure VS Code to validate your JSON files against the schema definitions. This will show validation errors in your editor and provide IntelliSense. To do so add the following configuration to your projects .vscode/settings.json:
{
"json.schemas": [
{
"fileMatch": ["catalogue*.json"],
"url": "./node_modules/@samply/lens/schema/catalogue.schema.json"
},
{
"fileMatch": ["options*.json"],
"url": "./node_modules/@samply/lens/schema/options.schema.json"
}
]
}
Test environment
It is a common requirement to load different options in test and production. You can achieve this by using a feature of SvelteKit that makes environment variables from the server available in the browser. Applications in the Samply organization commonly accept the following environment variables:
PUBLIC_ENVIRONMENT: Accepts the name of the environment, e.g.productionortestPUBLIC_SPOT_URL: Overwrites the URL of the Spot backend that your application queries
Just like you created a JSON file src/config/options.json, create a src/config/options-test.json (to start with, it can also contain an empty object {}).
Now you can handle these variables as follows:
<script lang="ts">
import type { LensOptions } from "@samply/lens";
import { env } from "$env/dynamic/public";
import optionsProd from "./config/options.json";
import optionsTest from "./config/options-test.json";
...
onMount(() => {
let options: LensOptions = optionsProd;
if (env.PUBLIC_ENVIRONMENT === 'test') {
options = optionsTest;
}
if (env.PUBLIC_SPOT_URL) {
options.spotUrl = env.PUBLIC_SPOT_URL;
}
setOptions(options);
});
...
</script>
Reading the query and showing results
When the user clicks the search button, a typical application will read the current query from the search bar, send the query to some kind of backend to get results, and then pass the results to Lens so it can show them.
Add the following to src/App.svelte to print the current query to the console when the search button is clicked and show some hardcoded results in a pie chart. Of course, in a real application the results would depend on the query. For example a user might want to know the gender distribution of people who are Rh positive.
<script lang="ts">
import { getAst, setSiteResult } from "@samply/lens";
window.addEventListener("lens-search-triggered", () => {
console.log("AST:", JSON.stringify(getAst()));
setSiteResult("berlin", {
totals: {},
stratifiers: {
gender: {
female: 9,
male: 3,
},
},
});
});
</script>
<lens-chart
title="Gender distribution"
dataKey="gender"
chartType="pie"
displayLegends="{true}"
></lens-chart>
You can read more about queries and the AST and about showing results in the dedicated guides.
Layout and design
We are maintaining a demo application in the Lens repository that showcases the layout and design of a typical application.
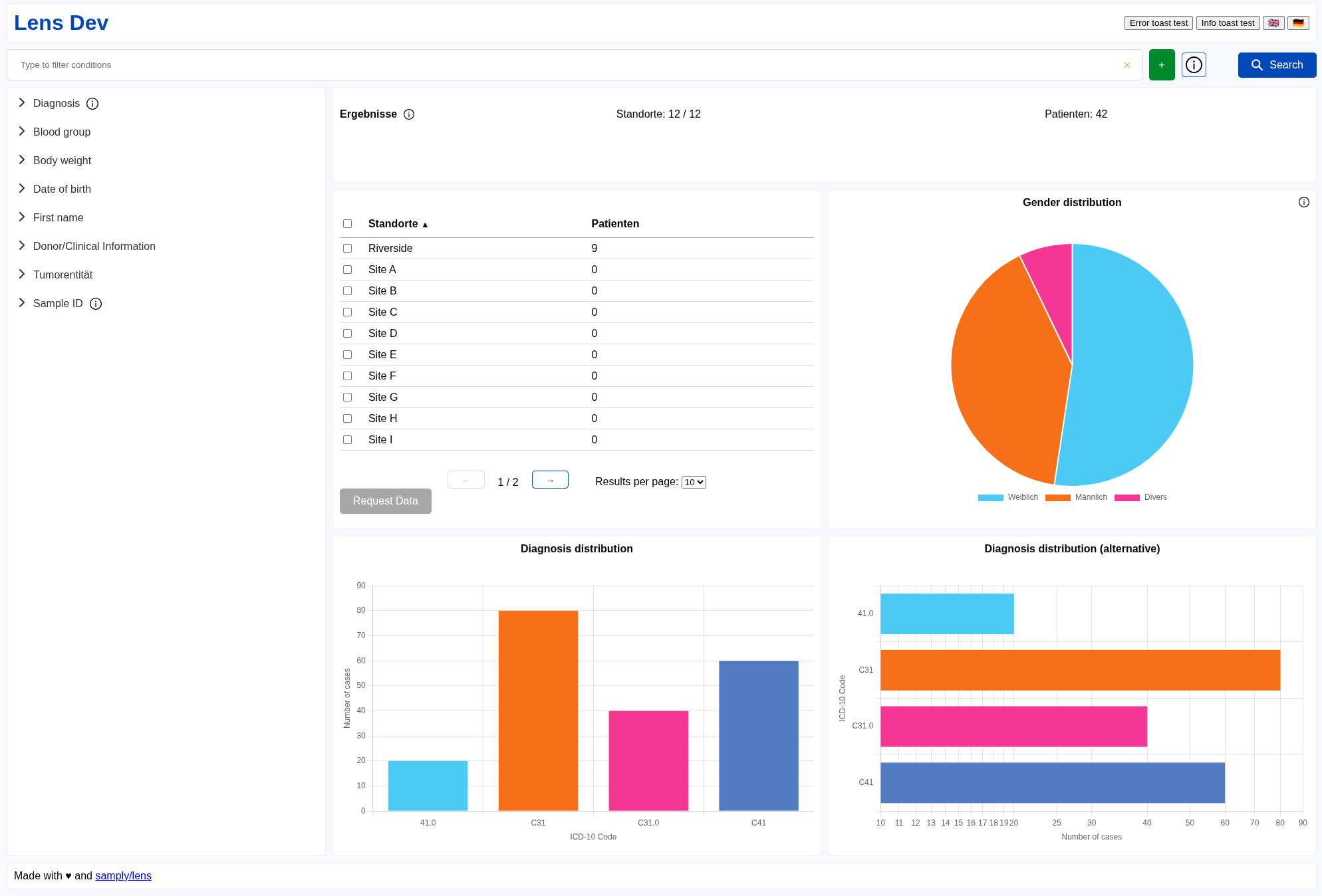
You can try out an interactive version here and find the source code in the demo.svelte file. The demo application uses a layout where the header and footer are always visible and the catalogue and main content areas are scrollable independently. You have the option to copy the layout or parts of the layout from the demo application and adapt them to your needs.
It is also possible to customize the styles of Lens components using CSS, see the overwriting styles guide for details.
Deploying using Docker
We recommend that projects in the Samply organization follow these deployment practices. We will use Node.js inside Docker. Run npm i -D @sveltejs/adapter-node and change the adapter in svelte.config.js:
-import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-auto';
+import adapter from '@sveltejs/adapter-node';
Then you can remove @sveltejs/adapter-auto from package.json. Now create a Dockerfile with the following content:
FROM node:22-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
# Install dependencies first to leverage Docker cache
COPY package.json package-lock.json ./
RUN npm ci
# Copy the rest of the application
COPY vite.config.ts svelte.config.js ./
COPY src ./src
COPY static ./static
# Build the SvelteKit project
RUN npm run build
# Production image
FROM node:22-alpine AS runner
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=builder /app/build ./build
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "build"]
GitHub Actions
You can use GitHub Actions to automatically run lints and build a Docker image when a pull request is opened or code is pushed. You can copy the following into .github/workflows/ci.yml and adjust it to your needs. It runs Prettier, ESLint, svelte-check (checks for TypeScript errors) and validates your catalogue and options JSON files. If these checks are successful it uses the Samply Docker CI to build a Docker image and push it to Docker Hub or the GitHub Container Registry.
name: CI
on:
pull_request:
push:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
linting:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v6
- run: npm ci
- run: npx prettier --check .
- run: npx eslint .
- run: npx svelte-check
- run: bash scripts/validate-json-schema.bash
docker:
needs: linting
uses: samply/github-workflows/.github/workflows/docker-ci.yml@main
with:
image-name: "samply/your-project"
#push-to: auto
#build-context: '.'
#build-file: './Dockerfile'
#build-platforms: "linux/amd64"
secrets:
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}
The catalogue
The catalogue contains all possible query elements used in your search or exploration application. Lens expects a catalogue to be provided during initialization — even an empty one is valid.
The structure of the catalogue is defined in schema and type. Validating your catalogue can be done within VS Code with the schema, see here.
Subgroups
The catalogue supports the definition of subgroups. For example, you might group all patients with diabetes at the top level, while also distinguishing between different types of diabetes. If a user wants to find patients with any form of diabetes, this can be expressed using subgroups in the catalogue.
Subgroups allow you to structure complex concepts in a way that supports both broad and narrow search criteria.
Querying a backend
Lens has two representations of the query in the search bar: the query store and the AST.
Query store
Once a user selects an element from the catalogue, it is added to the query store. The query store is of type QueryItem[][], where a QueryItem represents a chip in the search bar and the outer list represents a logical OR operation and the inner list a logical AND operation. Take for example this query:

The query searches for patients with blood group A+ and a body weight between 30 and 100 as well as patients with blood group B+ regardless of their body weight. In the query store this query is represented as follows:
[
[
{
"id": "10254884-b969-4bb2-8da9-d40eeb08586e",
"key": "blood-group",
"name": "Blood group",
"type": "EQUALS",
"values": [
{
"name": "A+",
"value": "A+",
"queryBindId": "7003ba31-2523-4e38-ba56-adf54dbf05cb"
}
]
},
{
"id": "babb673e-43ee-4e9b-8d81-0b7f3d1e41d3",
"key": "body_weight",
"name": "Body weight",
"type": "BETWEEN",
"values": [
{
"name": "30 - 100",
"value": {
"min": 30,
"max": 100
},
"queryBindId": "8ac6ad91-4f7a-4709-b701-eed7968ceb12"
}
]
}
],
[
{
"id": "4fc693e6-7865-4075-a84f-66afab0db7a0",
"key": "blood-group",
"name": "Blood group",
"type": "EQUALS",
"values": [
{
"name": "B+",
"value": "B+",
"queryBindId": "250d0bc1-b39d-47b0-98d8-e59a06797fd2"
}
]
}
]
]
Applications can read and write the query store using the getQueryStore and setQueryStore functions.
AST
To allow external systems such as databases and APIs to understand the query, the internal query store is transformed into an AST (Abstract Syntax Tree). The AST is a tree structure with the AstTopLayer type for branches and the AstBottomLayerValue for leaves. Generally the AST structure allows arbitrarily nesting AND and OR operations, although the AST as generated by Lens always has an outer OR operation and an inner AND operation to reflect the struture of the query store. The aforementioned query looks as follows in AST form:
{
"operand": "OR",
"children": [
{
"operand": "AND",
"children": [
{
"key": "blood-group",
"operand": "OR",
"children": [
{
"key": "blood-group",
"type": "EQUALS",
"value": "A+"
}
]
},
{
"key": "body_weight",
"operand": "OR",
"children": [
{
"key": "body_weight",
"type": "BETWEEN",
"value": {
"min": 30,
"max": 100
}
}
]
}
]
},
{
"operand": "AND",
"children": [
{
"key": "blood-group",
"operand": "OR",
"children": [
{
"key": "blood-group",
"type": "EQUALS",
"value": "B+"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
Applications can get the AST from the search bar using the getAst function.
Querying a Focus instance
In the samply organization Focus is commonly used to parse the AST and execute the query. Because Focus only communicates over the Beam protocol, Spot is required as an intermediary. Applications can query Focus by listening for the lens-search-triggered event and sending the AST to the backend in the appropriate form:
import { getAst, clearSiteResults, querySpot } from "@samply/lens";
let abortController = new AbortController();
window.addEventListener("lens-search-triggered", () => {
abortController.abort();
abortController = new AbortController();
clearSiteResults();
/** Helper function to base64 encode a UTF-8 string */
const base64Encode = (utf8String: string) =>
btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new TextEncoder().encode(utf8String)));
const query = base64Encode(
JSON.stringify({
lang: "ast",
payload: base64Encode(
JSON.stringify({ ast: getAst(), id: crypto.randomUUID() }),
),
}),
);
querySpot(query, abortController.signal, (result) => {
// This is called once per site when its result is received.
});
});
The querySpot function requires that you set the Spot URL in the Lens options:
"spotUrl": "https://locator-dev.bbmri-eric.eu/backend"
Usually Spot determines the list of sites to query via its SITES environment variable. You can optionally override the list of sites in the Lens options:
"sitesToQuery": ["lodz-test", "uppsala-test", "eric-test", "DNB-Test"]
Learn how to pass results to Lens in the Showing results guide.
Querying Focus with CQL
Some applications send CQL queries to Focus. In this case you need AST to CQL translation code in your application. You can get started by copying and adjusting the ast-to-cql-translator.ts, cqlquery-mappings.ts and measures.ts files from the CCP explorer repository. Sending the query would then look as follows:
import {
getAst,
clearSiteResults,
buildLibrary,
buildMeasure,
querySpot,
} from "@samply/lens";
let abortController = new AbortController();
window.addEventListener("lens-search-triggered", () => {
abortController.abort();
abortController = new AbortController();
// AST to CQL translation
const cql = translateAstToCql(
getAst(),
false,
"DKTK_STRAT_DEF_IN_INITIAL_POPULATION",
measures,
);
const lib = buildLibrary(cql);
const measure = buildMeasure(
lib.url,
measures.map((m) => m.measure),
);
/** Helper function to base64 encode a UTF-8 string */
const base64Encode = (utf8String: string) =>
btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new TextEncoder().encode(utf8String)));
clearSiteResults();
const query = base64Encode(
JSON.stringify({
lang: "cql",
lib,
measure,
}),
);
querySpot(query, abortController.signal, (result) => {
// This is called once per site when its result is received.
});
});
Showing results
Lens result format
When your application has queried a backend and receives results from sites, it has to pass these results to Lens so it can display them. Lens expects results of type LensResult, for example:
{
"stratifiers": {
"gender": {
"female": 31,
"male": 43
},
"diagnosis": {
"C34.0": 26,
"C34.2": 28,
"C34.8": 25
}
},
"totals": {
"patients": 74,
"samples": 312
}
}
The totals field contains the total number of patients, samples, etc. The stratifiers field contains stratum counts (e.g. male, female) for each stratifier (e.g. gender). The specific stratifiers depend on the application. When you add a chart to your application you specify which stratifier it should display.
Focus can return the Lens result format directly. If you are quering a FHIR server you can convert a FHIR measure report to the Lens result format using the measureReportToLensResult function.
Passing results to Lens
You pass results to Lens using the setSiteResult function. Before you pass a result you may call markSiteClaimed to indicate that the site is available and will deliver results soon. If a site that was claimed fails you can use removeFailedSite to hide the site from the result summary and result table and remove the site out of the resultstore. This examples shows how you would pass results from Focus to Lens.
querySpot(query, abortController.signal, (result: SpotResult) => {
const site = result.from.split(".")[1];
if (result.status === "claimed") {
markSiteClaimed(site);
} else if (result.status === "succeeded") {
const siteResult = JSON.parse(atob(result.body));
setSiteResult(site, siteResult);
} else {
removeFailedSite(site);
console.error(
`Site ${site} failed with status ${result.status}:`,
result.body,
);
}
});
Handling Empty Query Results
Sometimes a query may succeed but return no data, with totals of 0 and empty stratifiers. In these cases, it’s recommended to check for an empty result and inform the user.
Include this function:
export function isLensResultEmpty(result: LensResult): boolean {
// Check for non-empty stratifiers
for (const stratifier of Object.values(result.stratifiers)) {
if (Object.keys(stratifier).length > 0) return false;
}
// Check for non-zero totals
for (const value of Object.values(result.totals)) {
if (value !== 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
And check in your result function:
if (isLensResultEmpty(result)) {
showToast("No results found for your query", "info");
}
Components
Lens provides components to render results.
Overwriting styles
All Lens components have a unique part attribute that you can use in your application to overwrite styles. We try our best to keep the names of part attributes stable but keep in mind that sometimes we will have to change the structure of a component which will likely break your style overrides.
For example overwrite the color of the search button as follows:
::part(lens-search-button) {
background-color: red;
}
::part(lens-search-button):hover {
background-color: salmon;
}
Translations
Lens supports English and German language out of the box. You can set the language to en or de in the Lens options:
"language": "de"
Overwriting texts
You can overwrite the built-in translations in the Lens options to customize the text:
"texts": {
"loading": {
"en": "Processing..."
}
}
Or add translations for new languages:
"texts": {
"loading": {
"es": "Cargando..."
}
}
Or you can add your own texts that you can then translate in your application. We recommend that you prefix the key with your project name to avoid collisions:
"texts": {
"ccp-welcome": {
"en": "Welcome to CCP Explorer!",
"de": "Willkommen beim CCP Explorer!"
}
}
Using translations in your application
You can also use the translations in your application:
<script lang="ts">
import { translate } from "@samply/lens";
</script>
<span>{translate("loading")}</span>
Chart reset button
This is how you would implement a reset button using the resetDiagrams function.
<script>
import { resetDiagrams } from "@samply/lens";
</script>
<!-- example for a simple button-->
<button class="reset-button" onclick="{resetDiagrams}">Reset</button>
<!-- styling to fit with the rest/other buttons -->
<style>
button.reset-button {
background-color: var(--button-background-color);
color: var(--button-color);
border: none;
border-radius: var(--border-radius-small);
padding: var(--gap-xs) var(--gap-s);
font-size: var(--font-size-m);
cursor: pointer;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: var(--gap-xs);
}
</style>
Facet counts
Interace for displaying facet counts - the number of search results that would be returned when filtering by specific criteria. These counts are also displayed in the catalogue. Data can be populated using setFacetCounts() or sourced directly from a Spot instance.
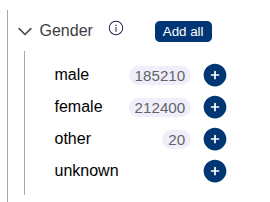
To enable facet counts add the following to the Lens options:
"facetCount": {
"hoverText": {
"gender": "Matching patients for this criterion only",
"diagnosis": "Total number of this diagnosis across all patients",
"sample_kind": "Matching samples for this criterion only"
}
},
hoverText controls the text that is displayed when hovering the mouse over the number chips. You also have to set the Spot URL in the Lens options:
"spotUrl": "https://locator-dev.bbmri-eric.eu/backend"
Lens POSTs an array of sites (e.g. {"sites": ["berlin", "munich"]}) to the appropriate Spot endpoint and expects facet counts in the following format:
{
"diagnosis": {
"C34.0": 26,
"C34.2": 28,
"C34.8": 25
},
"gender": {
"female": 31,
"male": 43
}
}
Development
Git hooks
The repository uses Husky with lint-staged to lint your commits. Husky automatically sets up a git hook when you do npm install for the first time. When you git commit the commit message is checked to comply with Conventional Commits and your staged files (and staged files only) are verified with ESLint and formatted with Prettier. If there are any problems you will get an error at the time of commit. This has the advantage that you notice problems before creating a pull request and without having to wait for GitHub Actions (our CI tool) to complete.
Styling
Lens tries to be very customizable and thus all built-in styles should be overridable by applications. Styles in web components are usually scoped to the component and cannot be overwritten from the outside. Therefore all HTML elements in Lens should use the part attribute:
<button part="lens-search-button"></button>
This enables applications to override styles from the outside as follows:
::part(lens-search-button) {
background-color: red;
}
However the ::part(foobar) selector does not work when used in the .svelte component file itself. Therefore the convention in Lens is to use the [part~="foobar"] selector inside components:
[part~="lens-search-button"] {
background-color: blue;
}
This has several advantages:
- We can scope our CSS styles to the component which eases maintainability
- We don’t have to come up with and specify an additional
classname - We cannot forget to set
partattributes because we use them for ourselves for styling
Note that the old convention in Lens was to keep styles in a CSS file separate from the .svelte component. Many components still use the old convention but we are moving towards component scoped styles.
Making a release
The new version number must follow semantic versioning and look like X.Y.Z. To make a new release follow these steps:
- Create or update the release notes at
book/src/releases/vX.Y.Z.mdand make a PR to merge them into develop. The release notes should include a migration guide if there are breaking changes. - Run
npm run version X.Y.Zand make a PR to merge the resulting version bump commit into develop. - Make a PR to merge develop into main.
- Run
git push origin vX.Y.Zto publish the tag that was created bynpm run versionand start the CI release process. - Verify that CI successfully builds and releases to npm and creates a release on GitHub.
Components
Here we list all the Lens components:
- Catalogue
- Chart
- Info Button
- Search Modified Display
- Negotiate Button
- Query Explain Button
- Query Spinner
- Result Summary
- Result Table
- Search Bar
- Search Bar Multiple
- Search Button
Catalogue
The <lens-catalogue> component renders the catalgue in a collapsible tree structure. The catalogue can be optionally collapsible, and will auto-expand based on configuration. If the options includes a facetCount input, it automatically fetches and updates facet counts on mount.
This component loads all elements from the catalogue store and lensOptions, uses DataTreeElement for each node, and offers customizable toggle behavior. Styling is exposed through ::part() attributes.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
toggle | { collapsable?: boolean; open?: boolean } | { collapsable: true, open: false } | Controls whether the catalogue is collapsible and its default open state. |
Usage
<lens-catalogue
toggle={{ collapsable: true, open: true }}
></lens-catalogue>
For a more in depth description of the structure see catalogue guide.
Styling
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-catalogue | Main container of the catalogue |
lens-catalogue-wrapper | Wrapper around all top-level nodes |
lens-catalogue-toggle-button | The expand/collapse toggle button |
lens-catalogue-toggle-button-closed-icon | Icon when the catalogue is collapsed |
lens-catalogue-toggle-button-icon | The icon stlye |
lens-catalogue-toggle-button-open-text | The label next to the icon |
Chart
The lens-chart component provides a styled wrapper for visualizing data using Chart.js. It handles dynamic display behaviors like toggling chart visibility, showing hints, and rendering a fallback message when no data is available. Some Options are set via ChartOption and some are set via props.
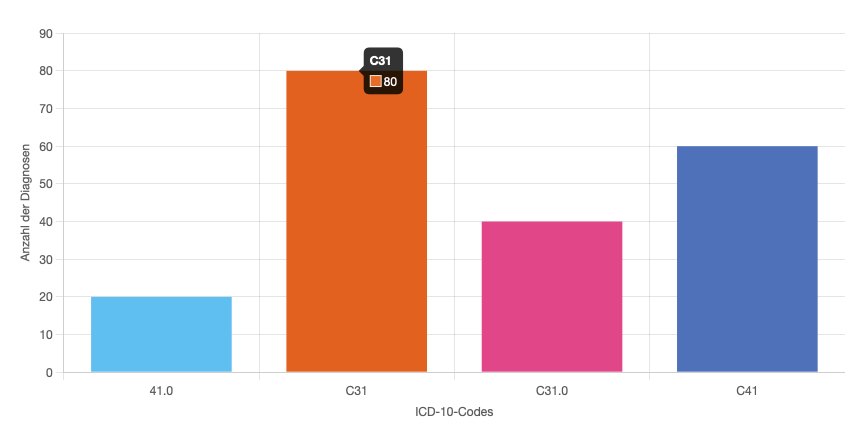
The component is constructed from a title and a chart. There is a slot after the title and chart for customization. The chart does render either totals or stratifier from the lens-results.
Props
Non of the props are required, however without datakey prop the chart does not known which data to render and will be empty.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | string | "" | Title displayed above the chart. |
indexAxis | string | "x" | Determines the main axis for data display. Use ‘y’ to flip the chart orientation (horizontal bars instead of vertical) |
xAxisTitle | string | "" | Title below the x-axis. |
yAxisTitle | string | "" | Title below the y-axis. |
clickToAddState | boolean | "false" | With this prop set to true it will add the clicked item to the search. The rendered element must have the same name as the catalogue item. |
headers | Map<string, string> | "" | Maps internal result keys to human-readable labels for display. For example, mapping “gender_m” to “Male” or “age_65_plus” to “65+ years”. |
displayLegends | boolean | "" | With this option a legend of all data items is render below the graph. |
chartType | ChartTypeRegistry | "" | Which type of chart is rendered, see types |
scaleType | string | "linear" | Sets the scale type of the chart. Either “linear” or “logarithmic” |
enableSorting | boolean | "false" | Enables sorting buttons for chart |
dataKey | string | "" | Looks up the data in the Result store. |
perSite | boolean | "false" | When true, displays aggregated totals per site/location instead of overall totals. |
groupRange | number | "" | lets the user define a range for the labels when only single values are used eg. ‘60’ -> ‘60 - 69’. |
groupingDivider | string | "" | Is the char that combines subgroups into their supergroups like C30, C31.1 and C31.2 into C31 |
filterRegex | string | "" | Filters data according to the provided regular expression. |
groupingLabel | string | "" | Sets divider for grouping stratifier together. |
viewScales | boolean | "true" | Displays the scales on the x-axis and y- axis. |
backgroundColor | string[] | "" | Expects an array with hex color strings. These colors will be set in the order which are provided. There is no possibility to map results to certain colors. If no color is set, there are the lens default colors. If you provide more results then colors, they will repeat from the beginning. |
hoverBackgroundColor | string[] | "" | Similar functionality as the background color, instead the hover colors. |
Example
<lens-chart
title="Gender"
datakey="gender"
chartType="pie"
displayLegends="true"
></lens-chart>
Styling
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-chart-wrapper | Root wrapper with grid layout and background color. |
lens-chart-info-button-wrapper | Positioned top-right; holds the optional info button. |
lens-chart-title | Renders the chart’s title, centered. |
lens-chart-overlay | Covers the chart area to display messages (e.g. no data). |
lens-chart-no-data-available | Styled message shown when there is no chart data. |
lens-chart-container-min-width-0 | Wraps the canvas; forces min-width: 0 for responsiveness. |
lens-chart-canvas | The chart rendering surface. Includes width/max-height rules. |
lens-chart-sort-buttons | The container for the sort buttons |
lens-chart-sort-button | Styling of a sort button |
lens-chart-sort-button:hover | Styling of a hovered sort button |
lens-chart-sort-button:active | Styling of an active sort button |
lens-chart-sort-button:focus | Styling of a focused sort button |
Info Button
The lens-info-button component displays a tooltip-style popup that provides users with helpful information or guidance. The popup is toggled by clicking the button.
This component is commonly used across various other components in Lens.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
message | string or string[] | "" | Text to display inside the tooltip. If an array is passed, each string will be rendered on a new line. |
buttonSize | number | 16 | Sets width and height of the button in px. |
alignDialogue | "top-left" | "top-center" | "top-right" | "bottom-left" | "bottom-center" | "bottom-right" | "bottom-center" | Controls where the tooltip appears relative to the button. |
dialogueMaxWidth | string | "300px" | Maximum width of the tooltip container. |
inSearchBar | boolean | false | Applies special styling when used inside a search bar (e.g., white icon with orange hover). |
Usage
Here’s a basic example of how to use the <lens-info-button> component:
<lens-info-button message="This will inform the user about the app!">
</lens-info-button>
Or with multiple lines:
<lens-info-button
message='["Line one", "Line two", "Line three"]'
buttonSize="{20}"
alignDialogue="top-right"
dialogueMaxWidth="250px"
>
</lens-info-button>
Styling
| Part name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-info-button | Styles the button container. |
lens-info-button-icon | Default icon styling. |
lens-info-button-icon-in-search-bar | Styling override when inSearchBar is true. |
lens-info-button-dialogue | Tooltip wrapper. |
lens-info-button-dialogue-message | Individual message lines. |
lens-info-button-dialogue-align-center | Tooltip center alignment. |
lens-info-button-dialogue-align-left | Tooltip left alignment. |
lens-info-button-dialogue-align-right | Tooltip right alignment. |
Example
lens-info-button::part(lens-info-button-icon) {
color: var(--primary-color);
}
About Lens
The lens-about component is optional but recommended for your application. It displays:
- A link to the Lens repository
- A short message: “Made with ♥”
- Additionally, it includes an info (“i”) icon. Clicking this icon opens a popover that shows the current version of the Lens library.
Search Modified Display
<lens-search-modified-display> displays a visual cue when the current query has been modified:

Usage
Include it like this:
<lens-search-modified-display></lens-search-modified-display>
You can customize the text using translations:
"texts": {
"query_modified": {
"en": "My custom text"
}
}
Styling
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-query-modified-display-wrapper | Wraps the content and applies border and spacing |
Example
lens-search-modified-display::part(lens-query-modified-display-wrapper) {
background-color: var(--light-orange);
color: var(--dark-orange);
font-weight: bold;
}
Negotiate Button
The lens-negotiate-button component allows users to initiate a data request. It becomes active when one or more (site/data sources) are selected. Depending on the configuration, it either dispatches a general event or starts a negotiation through the BBMRI-ERIC Negotiator service. The button is disabled by default when no data source is selected. It fires a global lens-negotiate-triggered event when clicked.
Optionally integrates with the BBMRI-ERIC Negotiator when type is set to "Negotiator".
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | string | "Request Data" | The label shown on the button. |
type | string | "" | Determines the negotiation behavior. Use "Negotiator" to enable integration with BBMRI-ERIC. |
Behavior
-
The button is disabled when no data sources are selected (
datarequestsStoreis empty). -
Clicking the button always triggers a global browser event:
window.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent("lens-negotiate-triggered")); -
If
typeis"Negotiator", the internalbbmriNegotiate()function is also called, passing the current data request list.
Usage
<lens-negotiate-button type="Negotiator"></lens-negotiate-button>
Or with a custom label:
<lens-negotiate-button
type="Custom"
title="Start Request"
></lens-negotiate-button>
Styling
| Part name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-negotiate-button | Base button styling. |
lens-negotiate-button-active | Applied when the button is enabled and clickable. |
lens-negotiate-button-disabled | Applied when the button is inactive (no data selected). |
lens-negotiate-button-title | Styles the text inside the button. |
Example
lens-negotiate-button::part(lens-negotiate-button-active) {
background-color: var(--custom-green);
}
Query Explain Button
The lens-query-explain-button is a wrapper around the lens-info-button that displays a human-readable version of the current query. When the QueryStore is empty, the noQueryMessage is shown. If a specific queryItem is passed as a prop, it will display only that part in depth, showing all child elements.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
queryItem | QueryItem | undefined | If provided, a human-readable explanation of this query item is displayed. If not, the current global query from queryStore is used. |
noQueryMessage | string | "Search for all results" | Message shown when no query is present. |
Usage
<lens-query-explain-button></lens-query-explain-button>
Styling
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-query-explain-button | Styling for the button around the InfoButton component |
lens-query-explain-single-row-message | Styling for a single queryItem element (string, number, etc.) |
lens-query-explain-multi-row-message-heading | Styling for the heading of multiple queryItems (e.g., array display) |
lens-query-explain-multi-row-message-heading-top | Styling for the top-level heading of multiple queryItems |
lens-query-explain-multi-row-message-group | Styling for grouping multiple queryItems |
lens-query-explain-header | Styling for the header of the explain box |
lens-query-explain-groups | Container styling for logical groupings |
lens-query-explain-group-item | Styling for individual group items |
lens-query-explain-bottom-level-items | Container styling for bottom-level elements |
lens-query-explain-bottom-level-item | Styling for individual bottom-level items |
lens-query-explain-bottom-level-item-header | Styling for headers of bottom-level items |
lens-query-explain-bottom-level-item-entry | Styling for entries within bottom-level items |
Example
lens-query-explain-button::part(lens-query-explain-button) {
border-color: var(--primary-color);
padding: 8px;
}
Query Spinner
The <lens-query-spinner> component provides a visual indication that a query is currently being processed. It automatically displays a spinning loader when a search is triggered and hides it once responses have been received from all data sources. The spinner listens on lens-search-triggered event and waits till all LensResults are not claimed anymore.
Usage
The spinner appears when a search is in progress and disappears once all site responses are received.
<lens-query-spinner size="24px"></lens-query-spinner>
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| size | string | 20px | Sets the height and width of the spinner |
Result Summary
The lens-result-summary component displays a compact summary of result metrics defined in the Lens options. It is typically used to show overall values, such as the total number of patients found across all data sources or how many sources responded successfully.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
indicateApproximation | boolean | false | Visually indicate that values are approximations (e.g., with a tilde). |
Example
To use the component, define the configuration in the Lens resultSummaryOptions (as described in the Options and catalogue section):
"resultSummaryOptions": {
"title": "Results",
"infoButtonText": "This is a tooltip",
"dataTypes": [
{
"title": "Patients",
"dataKey": "patients"
}
]
}
Usage
The component (which doesn’t use any props) can then be included in your HTML:
<lens-result-summary></lens-result-summary>
CSS Parts
This component uses ::part() selectors to expose internal styles for customization.
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-result-summary | Grid wrapper for the entire result summary layout. |
lens-result-summary-header | Container for the title and optional info button. |
lens-result-summary-heading | Alignment wrapper for the heading text. |
lens-result-summary-header-title | Flex layout for the header text and info button. |
lens-result-summary-content | Flex container for the individual population summaries. |
lens-result-summary-content-type | Holds each population title and its respective count. |
Styling Example
[part~="lens-result-summary-header"] {
background: #126154;
}
Result Table
The lens-result-table component displays a paginated and sortable table of totals from the LensResult. It uses the configured Lens options and listens to the ResultStore.
The table is setup with some props and some via the options. For example the columns are defined in the table options.
The table is automatically populated with data sources that are marked as claimed in the ResultStore. You can provide user-friendly labels for internal site keys via the siteMappings option.
If a data source has not yet been fully claimed, the table shows a “loading” message. This message is customizable via the translation key loading, see translation.
Each row includes a checkbox to select that data source for a data request. The selection is tracked in the DataRequestStore.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | string | "" | Optional title displayed above the table. |
pageSize | number | If set, limits the number of rows displayed and enables pagination. | |
indicateApproximation | boolean | false | Visually indicate that values are approximations (e.g., with a tilde). |
Slots
| Slot Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-result-above-pagination | Renders content above the pagination controls. |
beneath-pagination | Renders content below the pagination controls. |
Example
To use the table, define the configuration in the Lens tableOptions (as described in the Options and catalogue section):
"tableOptions": {
"headerData": [
{
"title": "Sites",
"dataKey": "site"
},
{
"title": "Patients",
"dataKey": "patients"
}
]
}
Usage
The component can then be included in your HTML:
<!-- Table in unpaged mode shows all rows and grows dynamically with the number of rows -->
<lens-result-table></lens-result-table>
<!-- Table in paged mode limits the number of rows per page and has fixed height -->
<lens-result-table pageSize={10}></lens-result-table>
Styling
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-result-table-title | The title heading above the table. |
lens-result-table | The table element itself. |
lens-result-table-header | The <thead> element. |
lens-result-table-header-row | The header row <tr>. |
lens-result-table-header-cell | Generic header cells. |
lens-result-table-header-cell-checkbox | Header cell containing the “select all” checkbox. |
lens-result-table-header-datatype | Header cells for data type columns (sortable, may include info buttons). |
lens-result-table-header-checkbox | The checkbox used to select all rows. |
lens-result-table-table-body | The <tbody> containing the data rows. |
lens-result-table-pagination | Container for pagination controls. |
lens-result-table-pagination-button | Previous and next arrow buttons. |
lens-result-pagination-pagination-previous | Specifically styles the “previous” button. |
lens-result-pagination-pagination-next | Specifically styles the “next” button. |
lens-result-table-pagination-pagenumber | Displays the current page number and total page count. |
Search Bar
The lens-searchbar component offers an interface for exploring of all catalogue items. It serves as the primary interface for users to search, apply, and adjust query criteria. Selected items appear as interactive chips within the component, giving users a clear visual of their active filters. Users can easily refine their search by removing individual values or entire criteria directly from the chip display.
Behavior & Functionality
-
Search Input with Autocomplete:
- Opens dropdown after 3+ characters.
- Filters and displays grouped suggestions with optional counts and descriptions.
- Keyboard navigation support (
focusedItemIndex).
-
Search Chips:
- Displays selected criteria as removable chips.
- Nested value-level and item-level delete buttons.
- Each chip displays:
- Criterion name
- Values
- Optional explain button via
QueryExplainButtonComponent
-
Autocomplete Items:
- Rendered with bold-highlighted matches.
- Supports facet counts from
$facetCounts. - Fully keyboard- and mouse-navigable.
-
Clear Group Button:
- Clears the entire group when clicked.
- Emits a
clear-searchevent.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
noMatchesFoundMessage | string | "No matches found" | Message shown when no autocomplete options are found. |
typeMoreMessage | string | "Search will start with 3 inserted letters" | Message shown when input is too short for autocomplete. |
placeholderText | string | "Type to filter conditions" | Placeholder in the search input field. |
index | number | 0 | Used to manage multiple search bars (e.g., in groups or filters). |
Example
<lens-search-bar
placeholderText="Search filters..."
noMatchesFoundMessage="No criteria match"
typeMoreMessage="Type at least 3 characters to search"
index="{1}"
/>
Styling
| Part | Purpose |
|---|---|
lens-searchbar | Wrapper for the entire component |
lens-searchbar-active | Active searchbar |
lens-searchbar-chips | Visual query chip wrapper |
lens-searchbar-chip | Query chip |
lens-searchbar-chip-name | Query chip criterion name |
lens-searchbar-chip-item | Query chip values wrapper |
lens-searchbar-chip-item-text | Query chip singular value |
lens-searchbar-input | Main input element |
lens-searchbar-input-options-open | Main input when autocomplete is open |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options | Autocomplete container |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-heading | Autocomplete group heading |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item | Individual result |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-focused | Highlighted result |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-criterion | Single select result |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-numeric | Numeric result input wrapper |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-date | Date result input wrapper |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-string | String result input wrapper |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-name | Option name |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-description | Optional description |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-description-focused | Focused optional description |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-item-facet-count | Facet count badge |
lens-searchbar-autocomplete-options-type-more-message | Wrapper for type more message |
Seach Bar Multiple
The lens-search-bar-multiple is a wrapper for multitple searchbars.
Each search bar is visually separated by an “or” indicator, and users can append additional bars using a dedicated add button. It is primarily used for OR-based query logic where each search bar represents an independent branch of the search criteria.
A default <slot /> is provided to insert additional UI elements, such as a search or submit button.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
noMatchesFoundMessage | string | "No matches found" | Message shown when no autocomplete options are available. |
placeholderText | string | "Type to filter conditions" | Placeholder text used across all search bars. |
Example
You may also include a search button using the default slot:
<lens-search-bar-multiple>
<lens-search-button title="Apply Filter"></lens-search-button>
</lens-search-bar-multiple>
Styling
The component exposes styling hooks via part attributes for full control over layout and appearance.
| Part | Purpose |
|---|---|
lens-searchbar-multiple | Wrapper around the full multi-search component |
lens-searchbar-multiple-wrapper | Wrapper for each search bar row |
lens-searchbar-multiple-add-button | Add button to insert a new search bar group |
lens-searchbar-multiple-or-indicator | Visual “or” indicator between search bars |
Search Button
The lens-search-button component triggers a search based on the current query. It is a visually styled button that emits an event when clicked. The button can be disabled via a prop, or will be disabled when a error state is entered in the searchbar.
Features
- Emits a event
lens-search-triggeredwhen clicked. With this event you would trigger some sort of data request for data provider.
Props
| Prop | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | string | "search" (localized) | The button’s visible label. Uses a translation helper by default. |
disabled | boolean | false | Whether the button is disabled and non-interactive. |
Usage
<lens-search-button></lens-search-button>
Styling
| Part name | Description |
|---|---|
lens-search-button | Main button container. |
lens-search-button-magnifying-glass | Icon shown at the start of the button (rotated magnifying glass). |
lens-search-button-title | Text label inside the button. |
Example
lens-search-button::part(lens-search-button) {
background-color: var(--primary-color);
}
lens-search-button::part(lens-search-button-magnifying-glass) {
font-size: 1.5rem;
color: var(--highlight);
}
Release notes
Version 0.6.3
Features
- Numeric range, date range, and string input catalogue entries can now be added and edited directly from the search bar without opening the catalogue.
- Charts now support sorting by value or alphabetically with visual toggle buttons that indicate sort direction. This feature is disabled by default and can be enabled by setting the
enableSortingprop of the Lens Chart component totrue. - Added functions
selectSiteandunselectSitethat allows to programmatically select sites in the table for data requests. - Added optional
indicateApproximationprop to result table and result summary components, that shows a visual indication that the numbers in the table/summary are approximations. - Added the About Lens component that provides a link to the Lens GitHub repository and shows the version of the Lens library that the application is currently running.
Breaking changes
- Removed unused
systemkey from catalogue, query store, and AST - Renamed
hideFailedSitetoremoveFailedSite - Changes to the
buttonSizeandalignDialogueprops of the Info Button component - Renamed
backgroundHoverColortohoverBackgroundColorin the charts props
Migration guide
Removal of system key
Remove the system key from your catalogues. It was unused before so nothing will break when you remove it.
Rename of hideFailedSite
Update your application to use removeFailedSite instead of hideFailedSite.
Changes to Info Button props
Update your info buttons to take numeric values instead of a string containing px on buttonSize prop.
Update your info buttons to take one of "top-left" | "top-center" | "top-right" | "bottom-left" | "bottom-center" | "bottom-right" on alignDialogue prop.
Version 0.6.2
Improvements
- Ability to hide failed sites: Added the
hideFailedSitefunction to allow applications to hide sites that have failed from the result summary and result table. Consider using this function in your result handling logic to improve user experience when dealing with site failures. See the Showing results guide for an example. - Enhanced Toast System: Introduced a unified toast component (
LensToast) that supports multiple toast types including error and info notifications with consistent styling and behavior - Query Explain Button Redesign: The redesigned query explain button now presents search details in user-friendly language with improved formatting and search bar chips displays query information in depth.
- The FacetCount is now settable via a function
Breaking Changes
- Component Rename:
error-toastcomponent has been replaced with the more versatilelens-toastcomponent - Function API Change:
showErrorToast()function has been replaced withshowToast(message, type)wheretypeacceptserrororinfo - Removed the
showInSearchbarprop as the component now automatically determines display behavior based on input context.
Migration Guide
Toasts
Update your HTML tags:
<!-- Before --->
<error-toast></error-toast>
<!-- After --->
<lens-toast></lens-toast>
Update your toast function calls:
// Before
import { showErrorToast } from "./toast";
showErrorToast("Something went wrong!");
// After
import { showToast } from "./toast";
showToast("Something went wrong!", "error");
showToast("Operation completed successfully!", "info");
Query Modified Component
The <lens-search-modified-display> component no longer has a <slot>. Remove any text inside the component tag and optionally customize the text using translations:
"texts": {
"query_modified": {
"en": "My custom text"
}
}
Result Table Pagination Changes
The page size switcher was removed so you should remove the pageSizeSwitcher prop if you were using it. The result table now operates in two modes:
<!-- Table in unpaged mode shows all rows and grows dynamically with the number of rows -->
<lens-result-table></lens-result-table>
<!-- Table in paged mode limits the number of rows per page and has fixed height -->
<lens-result-table pageSize={10}></lens-result-table>
Version 0.6.1
Improvements
- Enhanced Spinner Component: Improved visual feedback and performance
- Better URL Query Handling: More robust parsing and state management for URL parameters
- Refined Component Styling: Updated CSS for better visual consistency across components
- Enhanced Documentation: Expanded guides and improved code examples
Bug Fixes
- ResultTable: Fixed incorrect page size handling that could cause display issues
- Result Store: Resolved reactivity issues ensuring real-time data updates
Maintenance
- Dependencies: Updated all dependencies to their latest stable versions for improved security and performance
Migration Guide
This is a non-breaking release, no code changes required!
Version 0.6.0
Migration guide
New <lens-query-explain-button> component
In earlier versions of Lens, we used a specialized version of the <lens-info-button> to display the current query or a portion of it. This functionality has now been refactored into the dedicated <lens-query-explain-button> component. Update your app as follows:
-<lens-info-button noQueryMessage="Empty Query" showQuery={true}></lens-info-button>
+<lens-query-explain-button noQueryMessage="Empty Query"></lens-query-explain-button>
Querying the backend
In the new version, Lens will no longer query backends itself when the search button is clicked. Instead, the application must read the current query from the search bar, send the query to a backend to get results, and then pass the results to Lens so it can show them.
To give a short summary of the new paradigm, the application listens to the global lens-search-triggered event, then retrieves the current query using the new getAst function, optionally uses the new querySpot function to send the query to a backend, and then passes the results to Lens via the new markSiteClaimed and setSiteResult functions. More details and example code can be found in the Querying a backend and Showing results guides.
The setSiteResult function accepts the new LensResult format that is independent of the FHIR standard. The latest version of Focus can return the new result format directly. If you have a FHIR result you can convert to the new format using the measureReportToLensResult function.
A number of related APIs have been removed in favor of the new paradigm:
- The
backendfield has been removed from the Lens options - The
emit-lens-queryevent has been renamed tolens-search-triggeredand does no longer contain thedetailsfield - The
lens-responses-updatedevent has been removed
Catalogue prop changes
If you are using the collapsible catalogue feature, the texts for the expand/collapse button are now no longer specified as props:
<lens-catalogue
- texts={{
- collapseButtonTitle: 'My custom expand text',
- expandButtonTitle: 'My custom collapse text',
- }}
toggle={{ collapsable: true }}
></lens-catalogue>
If you specified any other texts in the texts prop you can remove them as well as they are no longer used. The expand/collapse button texts are now specified in the Lens options as translations:
"texts": {
"catalogue_expand": {
"en": "My custom expand text"
},
"catalogue_collapse": {
"en": "My custom collapse text"
},
}
The treeData prop previously used to provide the catalogue to Lens has been removed. Use the setCatalogue function instead.
CSS class name prefixes updated
Starting with version 0.6.0, all Lens CSS class names now begin with the prefix lens- followed by the component name.
This change improves readability, provides clearer structure, and helps avoid unintentional conflicts with existing styles or overrides.
If you are overriding any Lens component styles, please review your class names to ensure they match the new naming convention.
Query in URL
The URL now always updates to stay in sync with the current query so can share and bookmark queries via the URL. You can disable this in the Lens options:
"autoUpdateQueryInUrl": false
Removed iconOptions
Because this feature was rarely used icons in Lens can no longer be customized. Remove these lines from your Lens options:
"iconOptions": {
"deleteUrl": "delete_icon.svg",
"infoUrl": "info-circle-svgrepo-com.svg",
"toggleIconUrl": "right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg",
"addIconUrl": "long-right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg"
},
You can also remove the icon image files if your app does not use them anywhere else.
Removed <lens-data-passer>
The <lens-data-passer> component which was previously used to access a number of APIs has been removed. Most of these APIs have now been exported as regular TypeScript functions and some have been deprecated:
| Old API | Replacement |
|---|---|
getQueryAPI | getQueryStore |
getResponseAPI | Apps are now responsible for querying the backend so they have access to the responses without need for an API. |
getAstAPI | getAst |
updateResponseStoreAPI | setSiteResult, markSiteClaimed |
getCriteriaAPI | This API was previously used to resolve subgroups in the AST (e.g. replace C50.% with C50.1, C50.2, etc.). From Lens version 0.6.0 onwards the AST returned by getAst() already has subgroups resolved for you. |
getCatalogueAPI | Apps control the catalogue so there should be no need to read it from Lens. |
setQueryStoreAPI | setQueryStore |
setQueryStoreFromAstAPI | Only OVIS uses this API and we have provided a replacement for them but use of this function in new code is discouraged. |
addStratifierToQueryAPI | addItemToActiveQueryGroup |
removeItemFromQueryAPI, removeValueFromQueryAPI | If possible, use getQueryStore and setQueryStore instead. |
Removed <lens-options> component
The <lens-options> component has been removed. Instead use the setOptions and setCatalogue functions. When removing the <lens-options> tag you should also be able to remove the {#await} block that was needed previously. For example:
<script>
+ import {
+ setOptions,
+ setCatalogue,
+ type LensOptions,
+ type Catalogue,
+ } from "@samply/lens";
+ import options from "./config/options.json";
+ import catalogue from "./config/catalogue.json";
+ onMount(() => {
+ setOptions(options as LensOptions);
+ setCatalogue(catalogue as Catalogue);
+ });
- const jsonPromises = fetchData(optionsUrl, catalogueUrl);
</script>
-{#await jsonPromises}
- <!-- render a loading spinner -->
-{:then { optionsJSON, catalogueJSON }}
- <lens-options {catalogueJSON} {optionsJSON} {measures}></lens-options>
-{:catch someError}
- <!-- render the error -->
-{/await}
Renamed types
We’ve renamed some types to indicate that they are specific to the FHIR standard:
| Old name | New name |
|---|---|
SiteData | FhirMeasureReport |
Measure | FhirMeasure |
MeasureItem | FhirMeasureItem |
Facet counts use spotUrl
Facet counts now use the spotUrl from the Lens options with /prism automatically appended:
+"spotUrl": "https://locator-dev.bbmri-eric.eu/backend",
"facetCount": {
- "backendUrl": "https://locator-dev.bbmri-eric.eu/backend/prism",
"hoverText": {
"gender": "Matching patients for this criterion only",
...
}
},
Removal of catalogueKeyToResponseKeyMap option
In previous versions catalogueKeyToResponseKeyMap was used in the <lens-chart> component to map catalogue keys to response keys with different names. The map has been removed and the <lens-chart> component now takes the data key directly. Remove the map in the Lens options:
-"catalogueKeyToResponseKeyMap": [
- [
- "age_at_diagnosis",
- "donor_age"
- ],
-]
And update your usage of <lens-chart> accordingly:
-<lens-chart catalogueGroupCode="age_at_diagnosis">
+<lens-chart dataKey="donor_age">
Version 0.5.3
New features
- Exported
addItemToActiveQueryGroupto allow applications to programmatically add filters to the search bar
Migration guide
No breaking changes.
Version 0.5.2
New features
- Added an optional page size switcher to the result table
- Added facet counts to the catalogue
- Adjusted appearance of the autocomplete input to be consistent with other catalogue inputs
Migration guide
No breaking changes.
Version 0.5.1
Migration guide
We have changed the internal structure of most catalogue items. If your application overrides catalogue item styles you will likely have to adjust your styles.
Version 0.5.0
Lens version 0.5.0 paves the way for better documentation of the Lens library with the introduction of the Lens Book and API docs. Version 0.5.0 also introduces the translations API and the setOptions and setCatalogue APIs that pose an alternative to the <lens-options></lens-options> component. Finally it comes with internal improvements such as the migration to Svelte 5 and the automatic generation of the catalogue JSON schema to keep it in sync with the TypeScript definitions. You can find the full list of changes on GitHub.
Migration guide
Version 0.5.0 introduces a few breaking changes that application authors should be aware of. This guide will help you to migrate your application to the new version.
CSS bundle import path
The import path of the CSS bundle has changed. If the import is processed by your bundler we recommend to use automatic module resolution:
import "@samply/lens/style.css";
If you have to refer to the file directly you can find it at node_modules/@samply/lens/dist/lens.css.
Catalogue changes
The catalogue JSON schema is a little bit stricter now. Most notably every object with the "childCategories" property now additionally requires "fieldType": "group". For example:
{
+ "fieldType": "group",
"key": "donor",
"name": "Donor/Clinical Information",
"childCategories": [
...
]
}
You can use the following this script to update your catalogue. Afterwards open the file in your editor and reformat it.
sed -i 's/"childCategories"/"fieldType": "group", "childCategories"/' catalogue.json
Catalogue icons
Icons have been removed from the <lens-catalogue> component:
<lens-catalogue
- toggleIconUrl="right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg"
- addIconUrl="long-right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg"
- infoIconUrl="info-circle-svgrepo-com.svg"
...
></lens-catalogue>
Add them to the iconOptions object in the Lens options instead. Also remove the selectAll property and use the new translations API instead if you want to customize the text.
"iconOptions": {
"deleteUrl": "delete_icon.svg",
"infoUrl": "info-circle-svgrepo-com.svg",
+ "toggleIconUrl": "right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg",
+ "addIconUrl": "long-right-arrow-svgrepo-com.svg",
- "selectAll": {
- "text": "Alle Hinzufügen"
- }
}
Schema validation
JSON schema definitions for the Lens options and the catalogue are now included in the Lens release. Refer to this section in the new application guide to learn how to validate your JSON files against the JSON schema.